Tag Archives for " Autopilot "

Blue Button: Helping to Keep the Blue Side Up
Aircraft loss-of-control scenarios in-flight are one of the foremost safety concerns in aviation today. It’s become such a safety concern that it’s landed a spot on the National Transportation Safety Board’s Most Wanted List. At Garmin, we’re doing our part to help put an end to these dangerous events. And one of our tools is our “blue button.”

GMC 507 mode controller for GFC 500 digital autopilot, featuring the blue return-to-level mode button.
Officially referred to as the return-to-level (LVL) mode button, this dedicated button has been incorporated in select Garmin integrated flight decks featuring GFC 700, plus our new, cost-effective GFC 500 and GFC 600 retrofit autopilots — along with several Garmin autopilot solutions for experimental and light sport aircraft.
So, what exactly does the blue button do? In short, it puts the blue side — the sky — up. When the level mode button is activated in-flight, the autopilot automatically engages and works to return the aircraft to a straight-and-level condition.
We’ve heard the common scenarios that lead to loss of control before, including spatial disorientation from entering inadvertent IMC, from loss of situational awareness in the soup or even from steep turns. Fortunately, with our blue button, we’ve created a tool that can help.
For more information about the LVL Mode “blue button,” or to learn more about our autopilot solutions, visit our website at Garmin.com/aviation
Understanding Garmin Electronic Stability & Protection (ESP)
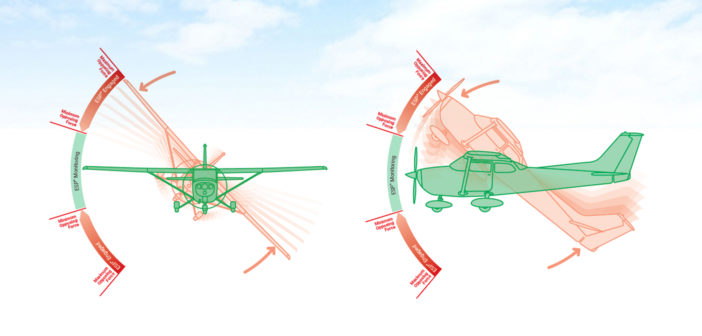
E-S-P. Three simple letters, with an extremely powerful meaning: Electronic Stability & Protection. It’s a feature our team designed to keep a watchful eye on an aircraft’s flight condition — and lend a helping hand if needed.
What is ESP? ESP is a safeguard created to assist you in maintaining safe, stable flight when hand-flying your aircraft. It monitors the aircraft’s flight condition, functioning independently of the autopilot, and it applies a control force toward stable flight whenever pitch or roll deviations exceed recommended limits. ESP can also recognize when underspeed or overspeed conditions are about to occur — such as a stall or too-steep of a descent — and it makes appropriate adjustments to the controls. Plus, if the system detects that ESP has been activated for a specified period of time — such as in the event of pilot incapacitation — the autopilot will engage with the flight director in level mode to bring the aircraft back to level flight. However, if you’re training or practicing, ESP can be manually disabled to allow intentional flight maneuvers.
Where is ESP? ESP can be found in many of our most popular integrated flight decks, including a number of G1000 NXi- and G3000-equipped aircraft, along with our new cost-effective GFC 500 retrofit autopilot for light single-engine aircraft, and GFC 600 retrofit autopilot for high-performance, more complex aircraft. Experimental/LSA owners and pilots can also take advantage of ESP with our G3X and G3X Touch experimental flight display systems by utilizing compatible G3X autopilot servos.
How can ESP help? Lately, an important discussion within the aviation community has centered around aircraft loss-of-control scenarios—in fact, it’s on the NTSB’s “Most Wanted” list. ESP is a direct result of these conversations. By helping to avoid the onset of inadvertent stall/spins, steep spirals or other loss-of-control situations, we want to help make the flight environment even better.
For more information about ESP, plus our extensive line of aviation products, visit our website at garmin.com/aviation.
